Here in this article, you’ll know that what is Reciprocating Pump, Rotary Pump, Air Lift Pump, & Jet Pump.
So let’s start without wasting much time.
Reciprocating Pump.
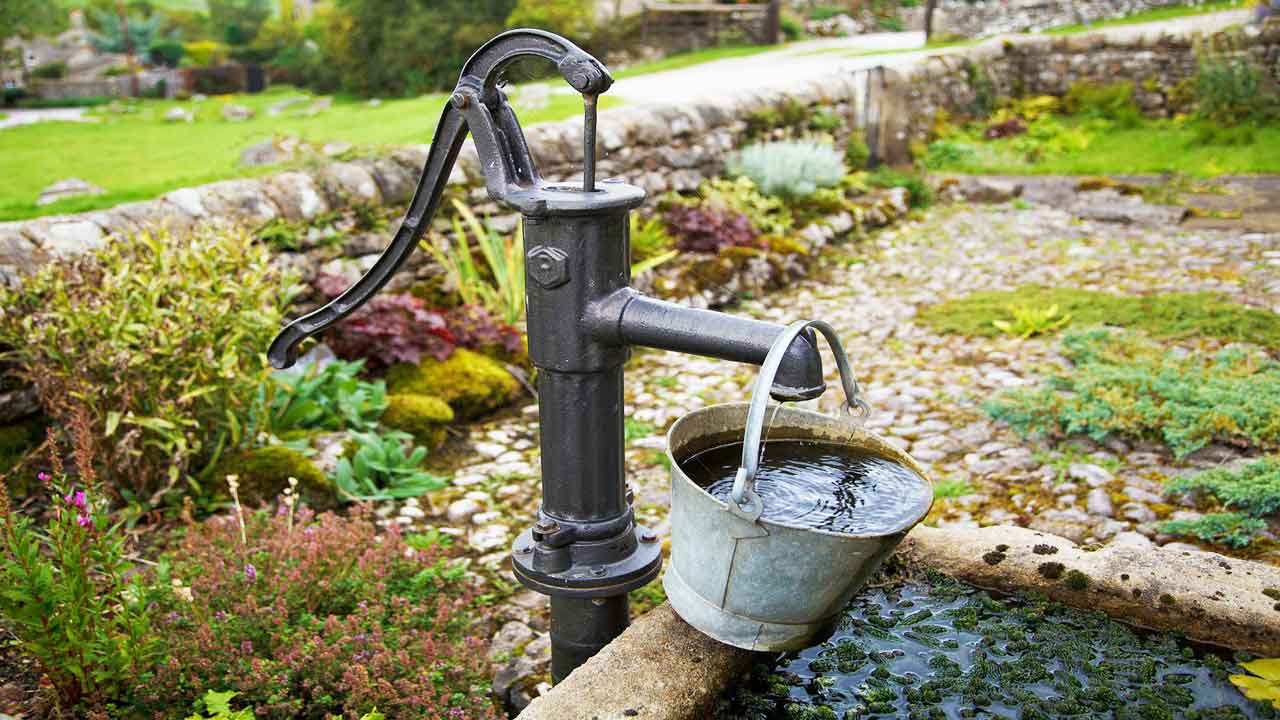
The simplest type of reciprocating pump is the hand-operated well pump. This pump must be primed before it will operate and is limited to suction lifts of about 20 ft.
On the down-stroke, the piston valve opens, permitting water to enter the space above the piston.
On the upstroke, the piston valve closes, and the water above the piston is lifted to the spout.
At the same time, the check valve opens, and water is drawn into the space below the piston.
By placing the piston cylinder in the well, perhaps even below the waterline, pumps of this type can develop a high lift.
The pump in the below picture is a single-acting pump in which discharge occurs only on alternate piston strokes.
Double-acting pumps discharge with each stroke and provide a more uniform flow.
Since a definite volume of water is discharged with each stroke, the delivery rate of a reciprocating pump depends only on the speed and is independent of the head.
The efficiency of a reciprocating pump depends upon the slippage or amount of water which leaks between the piston and the cylinder walls during a stroke.
If the valves and packing are in good condition, slippage should be less than 10 percent of total output.
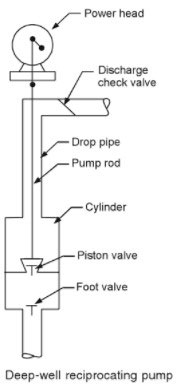
A deep-well reciprocating pump has three parts power head, cylinder, and drop pipe and rods.
The power head is usually at ground level directly over the well. The power head may be a steam cylinder or a crank shaft connected to a prime mover by gears or belt drive.
The cylinder, or pumping element, is placed in the well at the lowest expected water level.
The drop pipe transmits the water from the cylinder to the surface, while the rods transmit the oscillatory motion from the power head to the plunger.
A single-rod pump has one plunger, which may be either single or double acting.
The double-rod pump has two pump rods (a solid rod inside of a hollow rod) each of which connects to its own plunger.
The two plungers work one above the other in the same cylinder. Deep-well reciprocating pumps are widely used for oil wells.
A reciprocating pump must be primed before it will operate, and a supply of water for priming is generally provided in the installation.
Before starting a reciprocating pump, the discharge valve should be opened to prevent high pressures which may damage the discharge pipe or cylinder.
Many reciprocating pumps are provided with an air chamber on the discharge side of the pump.
The air in the chamber compresses and expands on each stroke to cause a more uniform flow in the discharge pipe.
Many large pumping stations equipped with reciprocating pumps were built during the nineteenth century.
Enormous pumping engines some as much as three stories high were employed.
The development of the electric motor and centrifugal pump provided a compact pumping unit which has virtually eliminated reciprocating pumps with their pulsating flow from water-supply service.
Centrifugal pumps are better suited to pumping water containing solids than are reciprocating pumps.
Generally, reciprocating pumps are advantageous only where high-head pumping is required or where their potentially higher efficiency overcomes their high initial and maintenance costs.
Read Also: What is Gravity Dam and its Construction?
Rotary Vane Pump.
The rotary vane pump is a displace merit pump consisting of two cams or gears which mesh together and rotate in opposite directions.
The rotating elements fit the casing closely, and the water trapped between them and the casing is forced through the pump as they rotate.
A definite amount of water depending on the size and shape of the gears or cams is passed with each revolution.
Water containing grit is very injurious to a rotary pump as the wear will destroy the seal between the cams and casing.
Rotary pumps are best adapted to low pressures with discharge less than 500 gpm (Gallon per Minute), although rotary pumps have operated at pressures up to 1000 psi and discharged over 30,000 gpm (Gallon per Minute).
Rotary pumps are self-priming and are often used to prime large centrifugal or reciprocating pumps.
The flow from a rotary pump is nearly free from pulsations. Since they have no valves, rotary pumps are simpler to construct and easier to maintain than reciprocating pumps.
The overall efficiency of rotary pumps is determined by the slip, or leakage, between rotor and casing.
The slip is determined by vacuum at suction, discharge pressure, and condition of the pump.
An increase of the vacuum at suction will reduce the efficiency of a rotary pump because gas entrained in the water will expand and occupy more of the pump displacement.
An increase in discharge pressure tends to force water back through the clearances to the suction side of the pump and results in lowered efficiency.
Rotary pumps are often used for fire-protection systems for buildings and for small domestic water systems.
Air Lift Pump.
An air lift pump uses compressed air to deliver water from wells. The air is forced into the well through a small air pipe and discharged into the eduction pipe at the bottom of the well.
The resulting mixture of air and water in the eduction pipe is lighter than the water outside the pipe and hence is forced upward by hydrostatic pressure.
This type of pump has been used for lifts as great as 500 ft, but its efficiency is usually only between 25 and 50 percent.
In spite of low efficiency, an air lift can deliver large amounts of water from small-diameter wells.
The air lift is not harmed by sandy water and is particularly suitable for use in crooked or damaged wells.
A separator is often placed at the discharge end of the eduction pipe to remove the air from the water.
The reclaimed air is usually cooler than atmospheric air and can be re compressed more cheaply.
An air lift pump is not adapted to raising water much above ground level, and if this is necessary, a second pump may be required.
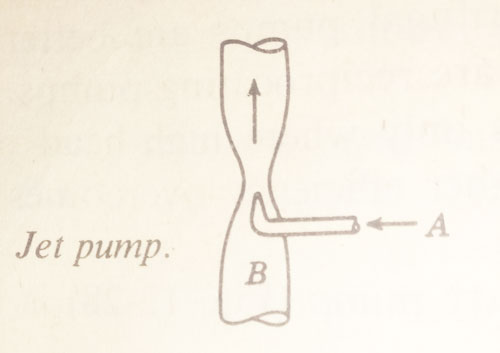
Jet Pump.
The jet pump, or ejector, is shown in the below picture. Steam, compressed air, or water forced through pipe ‘A’ discharges from a nozzle in the throat of pipe ‘B’ at high velocity.
The resulting jet creates a suction which draws the water up pipe ‘B.’
The efficiency of jet pumps is rarely over 25 percent, but they are compact, light in weight, and can handle muddy water.
Jet pumps are sometimes used in construction work for de-watering trenches and are widely used for pumping from small wells.
Thanks for reading. If you like this article don’t forget to share it.
Read Also: Earth Dam: Types of Earthen Dam and its Construction.


A diffusive siphon is a rotodynamic siphon that utilizes a pivoting impeller to build the pressing factor of a liquid. A stream siphon is fundamentally a divergent siphon mounted submerged and appended by a shaft to an engine mounted over the water and works by diverting water down to the admission to help lift the water. Thanks a lot for the nice post.